Logic gate
Logic gates are the basic building blocks of any digital
system. It is an electronic circuit having one or more than one input
and only one output. The relationship between the input and the output is based
on certain logic. Based on this, logic gates are named as
AND gate, OR gate, NOT gate etc.
There are basically seven types of logic gates, lets discuss
about them
1. NOT Gate
2. AND Gate
3. NAND Gate
4. OR Gate
5. NOR Gate
6. X-OR Gate
7. X-NOR Gate
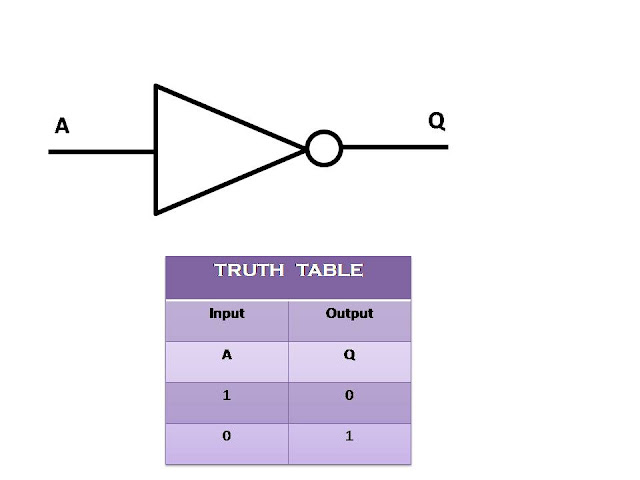
NOT Gate
A NOT gate provides a low output when the input is high and
high output when the input is low. Because of producing an opposite output as
compared to input it is also known as an Inverter.
Inverting NOT gates are single input devices which have an
output level that is normally at logic level “1” and goes “LOW” to a logic
level “0” when its single input is at logic level “1”, in other words it
“inverts” (complements) its input signal. The output from a NOT gate only
returns “HIGH” again when its input is at logic level “0” giving us the Boolean
expression of: A = Q.
AND Gate
An AND
gate is a digital logic gate with
two or more inputs and one output that performs logical conjunction. The output
of an AND gate is high only when all of the inputs are high. If one or
more of an AND
gate's inputs are low, then the output of the AND gate will be low.
NAND Gate
In digital electronics, a NAND gate (NOT-AND) is a
logic gate which produces an output which is low only if all its
inputs are high; thus its output is complement to that of an AND gate. A
LOW (0) output results only if all the inputs to the gate are HIGH
(1); if any input is LOW (0), the result will be a HIGH (1) output. NAND gate
is inverse of AND gate.
OR Gate
NOR Gate
The NOR gate is a digital logic gate that
implements logical NOR operation. A HIGH output (1) results if both
the inputs to the gate are LOW (0); if one or both input is HIGH (1),
a LOW output (0) is observed. NOR is the result of the negation of
the OR operator.
X-OR Gate
XOR gate (sometimes EOR, or EXOR and
pronounced as Exclusive OR) is a digital logic gate that gives a
true (1 or HIGH) output when the number of true inputs is odd. An XOR gate
implements an exclusive or; that is, a true output results if one, and
only one, of the inputs to the gate is true. If both inputs are false (0/LOW)
or both are true, a false output results. XOR represents the inequality
function, i.e., the output is true if the inputs are not alike otherwise the
output is false. A way to remember XOR is "must have one or the other but
not both".
X-NOR gate
The XNOR
gate (sometimes ENOR, EXNOR or NXOR and
pronounced as Exclusive NOR) is a digital logic gate whose
function is the logical complement of the Exclusive OR (XOR) gate. The
two-input version implements logical equality, behaving according to the
truth table to the right, and hence the gate is sometimes called an
"equivalence gate". A high output (1) results if both of the inputs
to the gate are the same. If one but not both inputs are high (1), a low output
(0) results.














No comments:
Post a Comment